*Central Nervous System
*Peripheral Nervous System
* Sensory Neurons
 *Sensory input allows information in
*Sensory input allows information in
 *Sensory input allows information in
*Sensory input allows information in
*Motor output allows response
-2 examples of this are the muscles, which control movement, and Glands,
which are secretion.
*Sensory controls our movement
*How our hands move
* When we pick up that cup
*Action Potentials
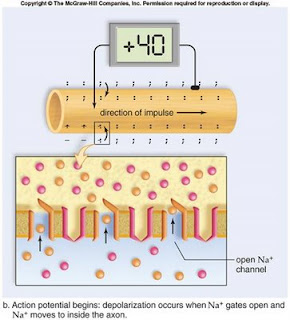
 *Ability to send a message similar to that of an animal
*Ability to send a message similar to that of an animal*Very common in nervous tissue cells called neurons and in muscle tissue
*Neurons
*The main cells in the nervous system
*Transmit messages
-Action Potentials
*Axon carries messages
*Single neurons carries messages to and from periphery
*A majority of neurons never die or divide after the initial nervous system development
*Myelin Sheath
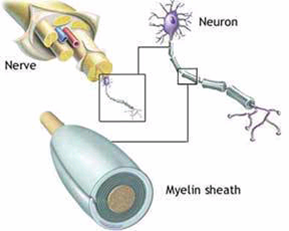
*Hundreds and thousands of axons are contained in a single nerve
*Myelin Sheath surrounds each axon
*Myelin Sheath is a fat-based insulating substance
*Myelin Sheath isolates neurons to help speed up the action potential propagation
*Sensory neurons
*Brings in information from everywhere but the spinal cord and brain
*Motor neurons
*take messages from spinal cord and brain
*Synapse
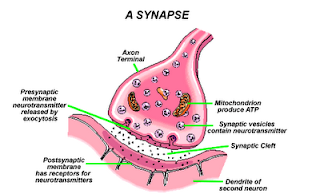
*Neurotransmitter is secreted to stimulate connecting neurons or muscle cells
*Sensory receptors respond to stimulus from body or environment
*visual cortex forms visual field or completevisual image* Sensory cortex maps touch sensation from entire skin surface
* in our head we have 5 senses
*Taste

*taste buds are located primarily on the tongue. Along the walls of the oaoillae are many taste buds as well. Isolated taste buds are also present on the hard palate, the pharynx, and the epiglottis. There are four primary types of taste: sweet, sour, salty, and bitter. There is a fifth flavor that exists in cheese, beef broth and some sea foods, its called umami. The tip of the tongue is the most sensitive to sweet taste. the margins of the tongue are most sensitive to salty and sour taste and the rear of the tongue to bitter taste.
 -the outer layer, sclera
-the outer layer, sclera
 *outer ear consist of the pinna and auditory canal
*outer ear consist of the pinna and auditory canal
*Vision
 -the outer layer, sclera
-the outer layer, sclera-cornea, made of transparent collagen fibers
-choroid, the middle,thin, darkly pigmented layer
-iris donut-shaped towards the front
-pupil a hole in the center of the iris through which light enters
-ciliary body contains the ciliary muscle, which controls the shape of the lens for near and far vision
-lens, attached to the ciliary body by suspensory ligaments
-aqueous humor is clear, watery fluid
-when someone has glaucoma, these drainage ducts are blocked
*Smell
*Smell
*80-90% of what we think is taste is actually due to our sense of smell.
*our sense of smell depends on between 10 and 20 million olfactory cells
* olfactory cells are located within the olfactory epithelium high in the roof of the
nasal cavity
*The brain receives odor information
*Hear
*Hear
 *outer ear consist of the pinna and auditory canal
*outer ear consist of the pinna and auditory canal*middle ear begins at the tympanic membrane and ends at a bony wall containing 2 small openings covered by membranes
*oval and round windows are the openings
*Ossicles are three small bones between the tympanic membrane and oval window
*malleus the hammer
*incus the anvil
*stapes the stirrup are what they are called individually
*Auditory tube extends from the middle ear to the nasopharynx
*inner ear has three areas
-semicircular canals
-vestibule
*both concerned with equilibrium
-cochlea
*concerned with hearing
*Equilibrium
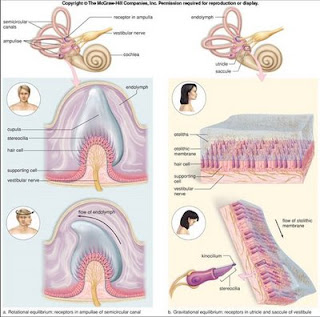 *The vestibular nerve arises in the semicircular canals, saccule, and utricle, takes nerve impulses to the brain stem and cerebellum. Through its communication with the brain, the vestibular nerve helps us achieve equilibrium, other structures in the body are also involved.
*The vestibular nerve arises in the semicircular canals, saccule, and utricle, takes nerve impulses to the brain stem and cerebellum. Through its communication with the brain, the vestibular nerve helps us achieve equilibrium, other structures in the body are also involved.
No comments:
Post a Comment