Skeletal System
*Bones
development
growth
repair
remodeling
*Joints
skeletal movement
mobility
lubrication
*Muscle
structure
cell structure
contraction
muscular disorders
homeostasis

*Functions of Skeleton
-supports the body
-protects soft body parts
-produces blood cells
-stores minerals and fat
-allows flexible body movement
*Anatomy of a Long Bone
-the shaft is called a diaphysis
-medullary cavity is contained in the diaphysis whose walls are composed of compact bone
-epiphysis is the expanded region at the end of the bone
-epiphyses are coated with a thin layer of hyaline cartilage, which is called articular cartilage due to it occurs at a joint
-spongy bone has an unorgaized appearence
-red bond marrow fills the spaces of a spongy bone
*Cartilage
-is not as strong as bone
-more flexible
-chondrocytes cells lie within lacunae that are irregularly grouped
*types of cartilage
*Hyaline
-firm
-somewhat flexible
*Fibrocartilage
-stronger than Hyaline
-can withstand pressure and tension
*Elastic
-more flexible than hyaline
-found in ear flaps
*Bones
Bones growth, remodel, and repair need involvment of a couple different cells
*Osteoblasts
-bone firming cells
-secrete organic matrix
-promote deposition of calcuim salts into the matrix
*Osteocytes
-mature blood cells
-derived from osteoblasts
-maintainbone structure
*Osteoclasts
-bone-absorbing cells
-break done bone
-assist in depositing calcuim and phosphate in the blood
*Bone development and Growth
-ossification
-formation of bone
-intramembranous ossification
-bone develop between sheets of fibrous connective tissue
-endochondral ossification
-bone replaces the cartilaginous models of the bone
-hormones affect bone growth
*Bone remodeling
-normally keeps bones strong
-bones can respond to stress
*Bone Repair
-required after it breaks or fractures
*It takes 4 stages to heal a fracture:
-Hematoma, blood escapes from ruptured blood vessels and forms a hematoma in the space between the broken bones within 6-8 hours
-Fibrocartilaginous callus fills the space between the ends of the broken bone for about 3 weeks after tissue repair begins
-Bony callus. Osteoblasts produce trabeculae of spongy bone and convert the fibrocartilage callus to a bony callus that joins the broken bones together and lasts about 3-4 months
-Remodeling. Osteoblasts build new compact bone at the periphery, and ostoclasts absorb the spongy bone, creating a new medullary cavity
*Skull
-formed by the cranium
-fontanels usually close by 16 months old by intramembranous ossification
-sinuses are air spaces lined by mucous membrane
-mastoiditis is a condition that can lead to deafness, is an inflammation of these sinuses
-frontal bone forms the forhead
-parietal bones extend to the sides
-occipital bone curves to form the base of the skull
-foramen megnum through which the spinal cord passes and becomes the brain stem
-sphenoid bone is shaped like a bat with outstreched wings
-ethmoid bone lies in front of the sphenoid
*facial bones
-mandible is the lower jaw
-maxillae are the bones that form the upper jaw
-zygomatic bones are the cheekbone prominence
-nasal bones form the bridge of the nose
*Hyoid bone
-not part of skull
-part of the axail skeleton
-attached to the temporal bones by muscles and ligaments and to the larynx by a membrane
*Synovial Joints
-a joint having a cavity filled with synovial fluid, a lubricant for the joint. Ligaments connect bone to bone and support or strengthen a joint. Fluid-filled sacs called bursae ease friction between bare areas of bone and overlapping muscles, or between skin and tendons.


*Types of muscles
-smooth muscle fibers are spindle-shaped cells
-cardiac muscle forms the heart wall
-intercalated disks contain gap junstions that permit contractions to spread quickly throughtout the heart wall
-skeleton muscle fiberes are tubular, multinucleated, and striated.
*Functions of muscles
-supports the body
-make bones move
-help maintain a constant body temperature
-contraction assists movement in cardiovascular and lymphatic vessels
-help to protect internal organs and stabilize joints

*Muscle Fibers
-sarcolemma, the plasma membrane
-the cytoplasm is the sarcoplasm; and the endoplasmic reticulum is the sarcoplasmic reticulum
-T tubules penetrate into the cell so that theycomes into contact but not fuse
-myofibrils contractile portions of the mucsle fibers
*Myofilaments
-thick filaments are composed of several hundred molecules of the protein myosin
-thin filaments consists of 2 intertwinning strands of protein actin
 *Testes
*Testes




 *Fertilization
*Fertilization


















 *Sensory input allows information in
*Sensory input allows information in
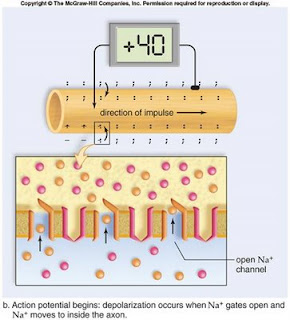
 *Ability to send a message similar to that of an animal
*Ability to send a message similar to that of an animal
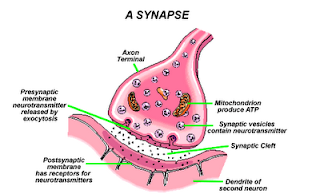

 -the outer layer,
-the outer layer,  *outer ear consist of the
*outer ear consist of the 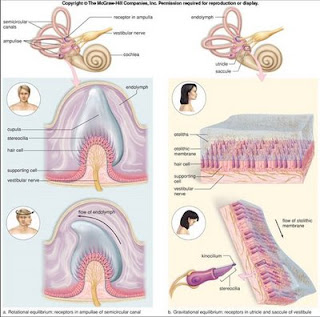 *The vestibular nerve arises in the semicircular canals,
*The vestibular nerve arises in the semicircular canals,